As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the various EV charging levels and connector types is crucial for both current EV owners and prospective buyers. With the ever-changing landscape of charging solutions, knowing how to charge your EV efficiently and cost-effectively is essential. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different EV charging levels, connector types, and future developments in EV charging technology, arming you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your charging needs.
Short Summary
- Understanding EV charging levels is key to making the most of your experience.
- Different connector types are available, including J1772 (universal), CHAdeMO, and CCS for DC fast charging, and Tesla connectors exclusive for Tesla vehicles.
- Home solutions vary depending on driving needs. Public/workplace costs must be understood before selecting a station. Future developments such as high-power AC & XFC have the potential to revolutionize the way we charge EVs.
Understanding EV Charging Levels

Navigating the world of EV charging can be a bit overwhelming, but it’s essential to grasp the three primary charging levels: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. Each level offers varying charging speeds and power outputs, catering to different charging needs and vehicle types.
So, whether you’re charging your electric vehicle at home or on the go, understanding these charging levels will ensure you make the most of your EV experience.
Level 1 Charging: Standard Household Outlets
Level 1 charging utilizes standard 120V household outlets and offers slow charging speeds, making it suitable for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) or occasional overnight charging for battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Level 1 charging has an output range between 1 kW and 1.8 kW, which can be considered a modest electric range. It provides 3-7 miles (4-11 kilometers) of range per hour of charging.
In North America, Level 1 charging uses a standard 3-prong household plug connected to a J1772 (Type 1) EV connector, making it compatible with all BEVs and PHEVs. While Level 1 charging may not be the fastest option, it serves as a reliable backup solution or a viable option for PHEV owners with smaller batteries.
Level 2 Charging: Faster Home and Public Charging
For those seeking faster charging speeds, Level 2 charging is the way to go. Utilizing 240V/208V electrical service, Level 2 charging is ideal for homes, workplaces, and public charging stations for BEVs. With its increased power output, Level 2 charging stations can be found at residences, workplaces, and various public sites such as hotels, retail parks, and supermarkets.
A Level 2 charger necessitates a dedicated 240-volt circuit. This is the same kind of circuit required by an electric clothes dryer or kitchen range. While Level 1 charging provides a modest boost to your EV’s range, Level 2 charging significantly reduces charging time, with PHEVs charging in just 1-2 hours.
Level 3 Charging: DC Fast Charging for Long Journeys
When you’re on a long journey or need a quick boost to your EV’s range, Level 3 charging, also known as DC Fast Charging, is your best bet. This rapid charging option is compatible with most BEVs but not PHEVs. Level 3 charging stations can provide 3 to 20 miles of range per minute, significantly reducing the time spent waiting for your EV to charge.
Although Level 3 charging offers impressive speed, the cost of installing a Level 3 charger can be substantial, ranging in the tens of thousands of dollars. Nevertheless, for those in need of a quick charge during a long journey or in high-traffic areas, Level 3 charging stations are a valuable resource.
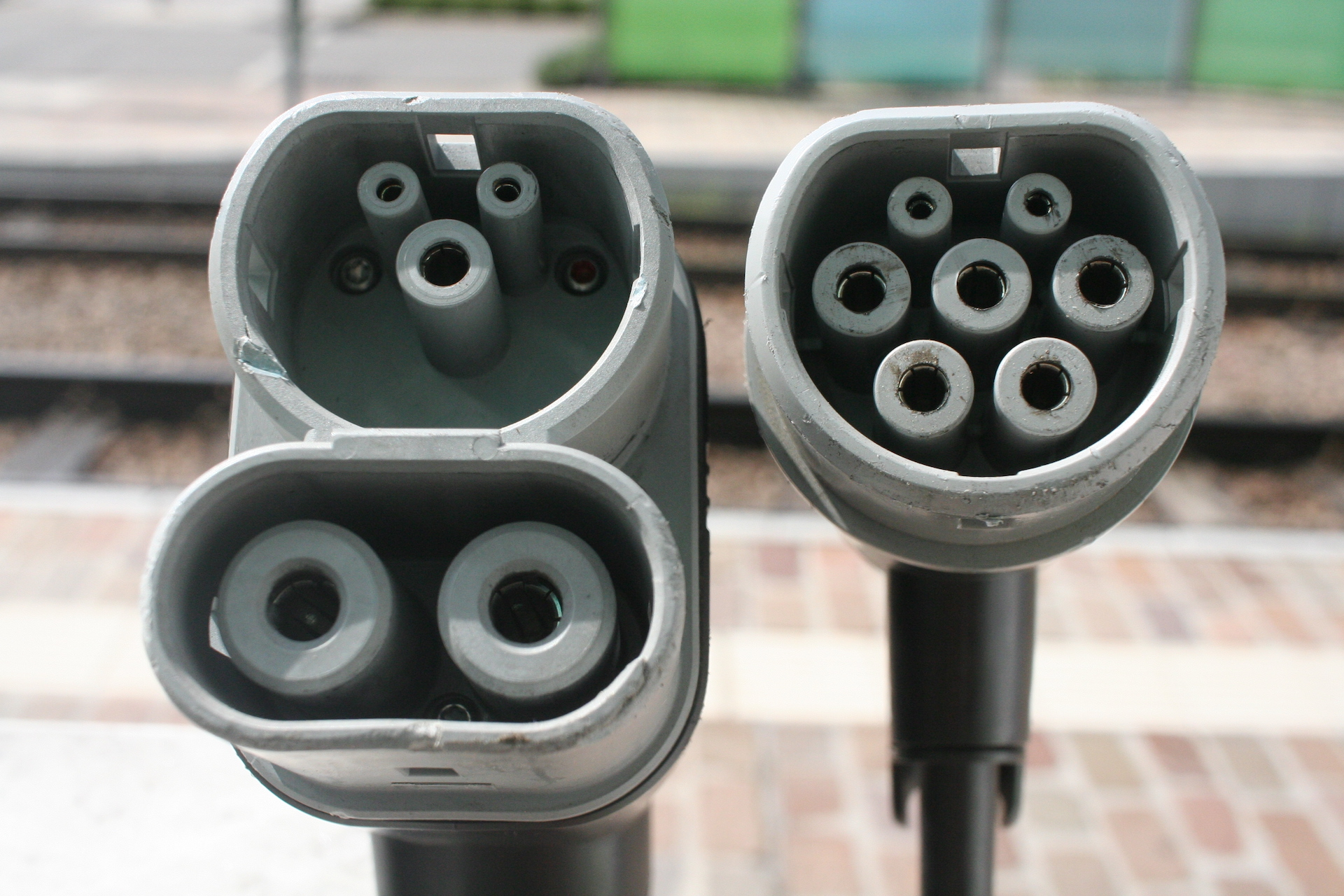
Connector Types and Compatibility
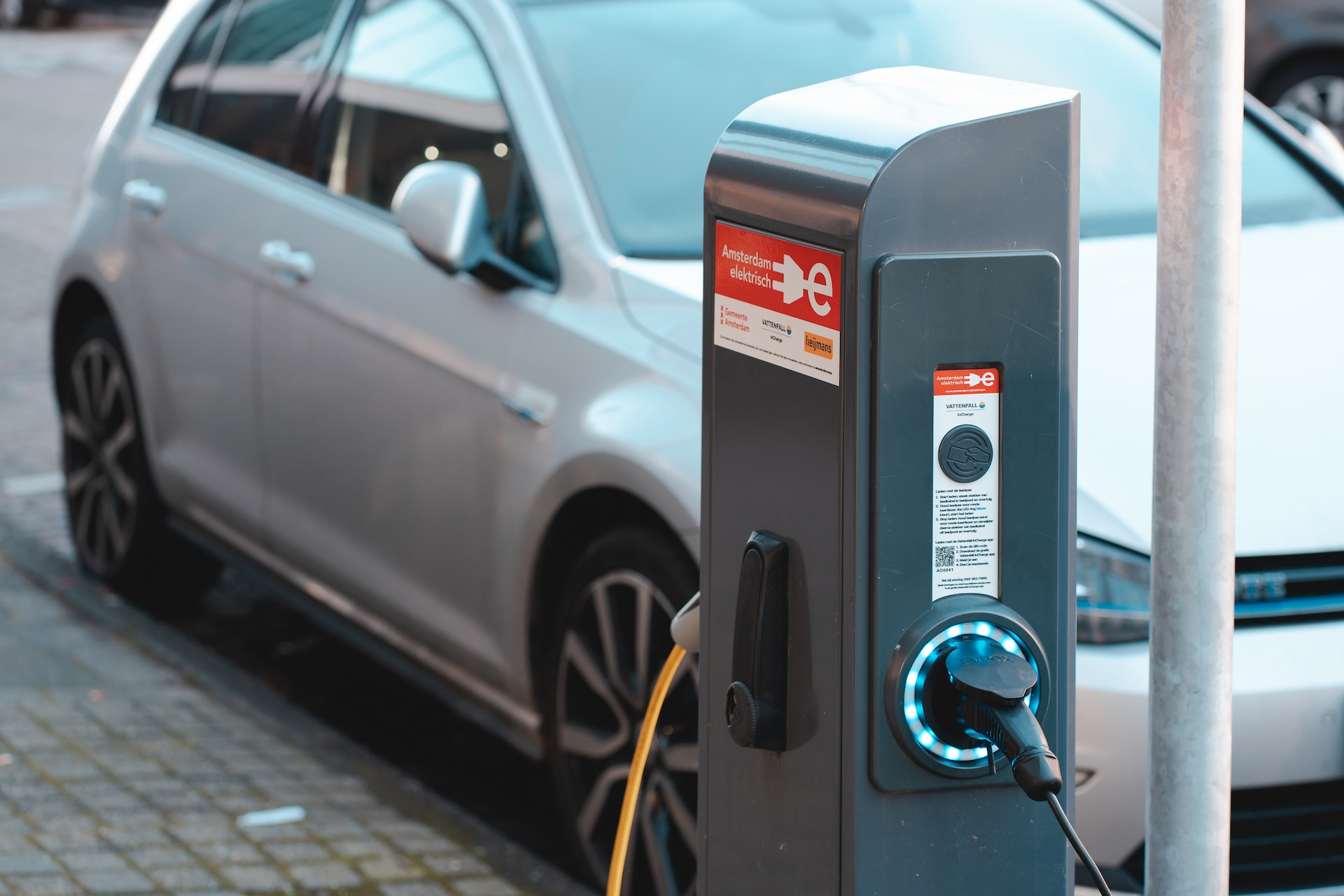

In addition to understanding the different charging levels, it’s important to know the various connector types used for EV charging. These connectors, which include:
- J1772
- CHAdeMO
- CCS
- Tesla connectors
Determine the charging level and vehicle compatibility.
In the following sections, we’ll explore each connector type and its compatibility with different EV models.
J1772: The Universal Connector
The J1772 connector, also known as the “J Plug,” is the universal connector for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America. Compatible with all electric vehicles, including plug-in hybrids, on the market (excluding Tesla), the J1772 connector ensures a seamless charging experience for most EV owners.
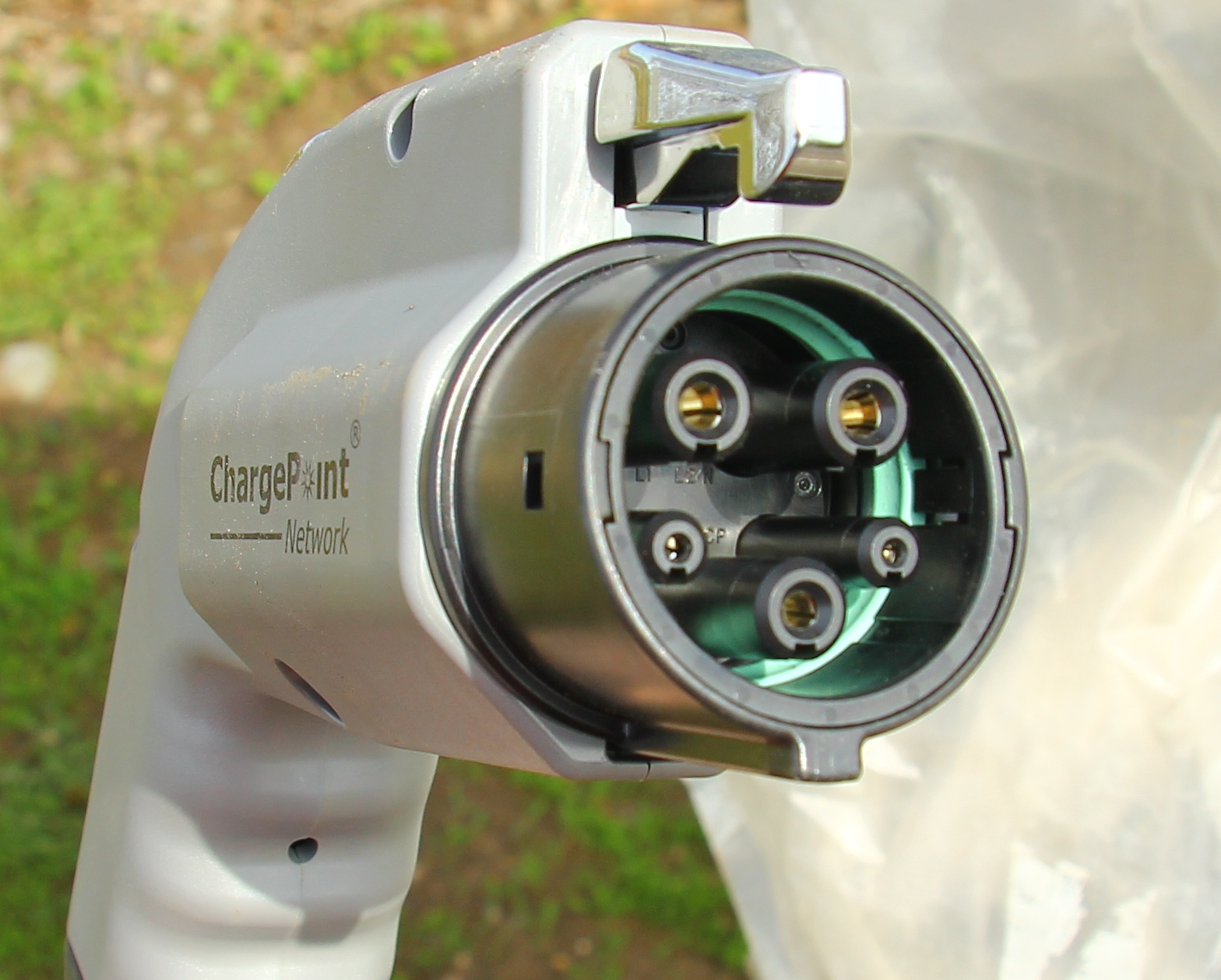

As the standard connector for both Level 1 and Level 2 charging, the J1772 connector provides a convenient and consistent charging solution for EV owners in North America. With its widespread adoption and compatibility, the J1772 connector remains a crucial component of the EV charging infrastructure.
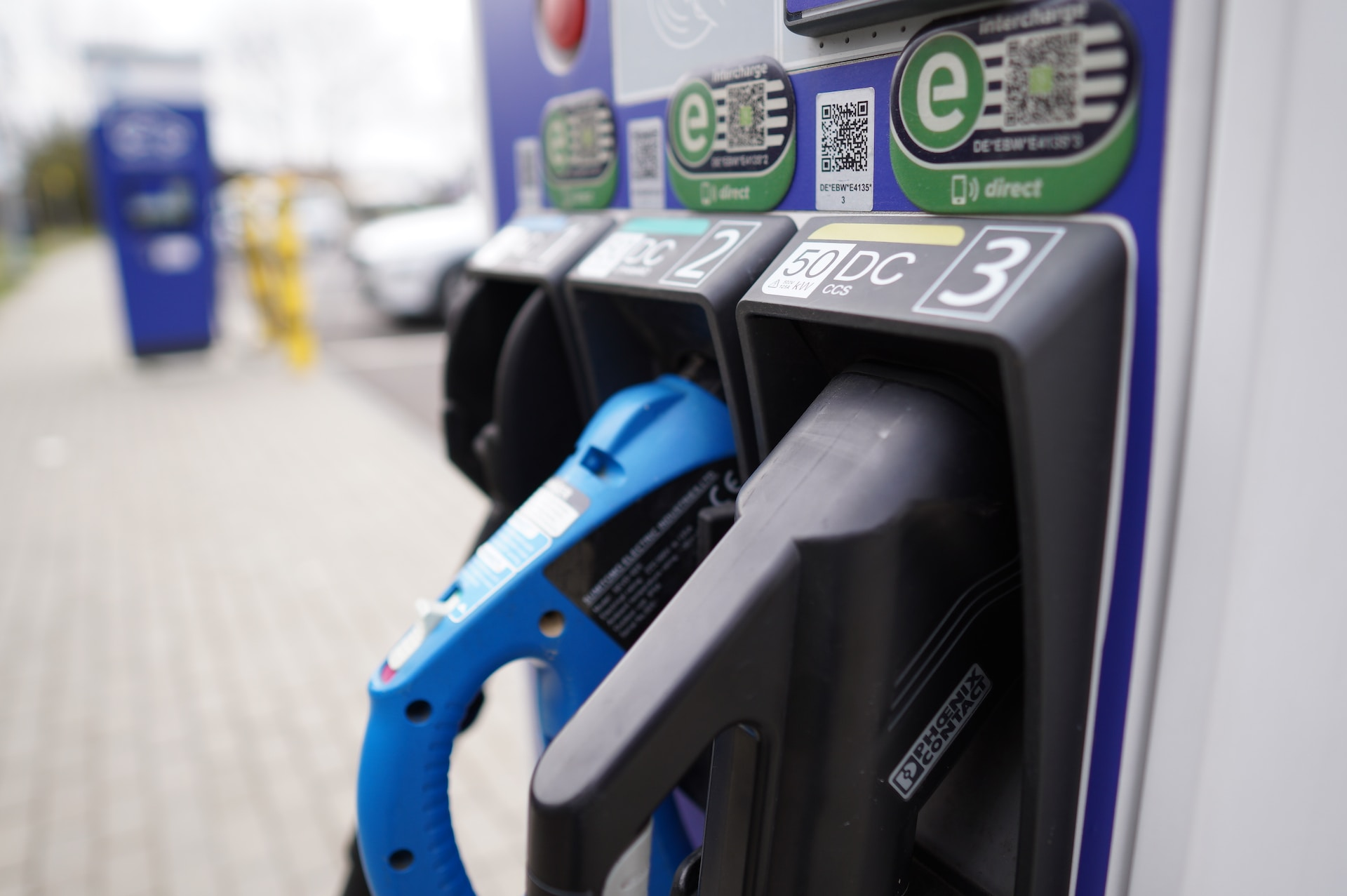
CHAdeMO and CCS: DC Fast Charging Standards

For Level 3 charging, there are two main DC Fast Charging standards: CHAdeMO and CCS. CHAdeMO is used by Nissan and Mitsubishi, while CCS is employed by all other manufacturers, excluding Tesla. These connectors enable rapid charging for compatible EVs, making long journeys more manageable and convenient.
While CHAdeMO and CCS connectors are not universally compatible across all EV models, their adoption for Level 3 charging has facilitated the expansion of DC Fast Charging infrastructure. As a result, more and more EV drivers can benefit from the speed and convenience of Level 3 charging stations.
Tesla Connectors: Exclusive for Tesla Vehicles
Tesla has developed its own proprietary connector for use with its vehicles, enabling both Level 2 and Level 3 charging at Tesla Superchargers. This unique connector is exclusively compatible with Tesla vehicles, providing a tailored charging experience for Tesla owners.
While the Tesla connector is not compatible with non-Tesla EVs, Tesla owners do have the option to use non-Tesla DC Fast Chargers with a $400 adapter. This flexibility allows Tesla drivers to access a wider range of charging options while on the road.

Home Charging Solutions: Making the Right Choice
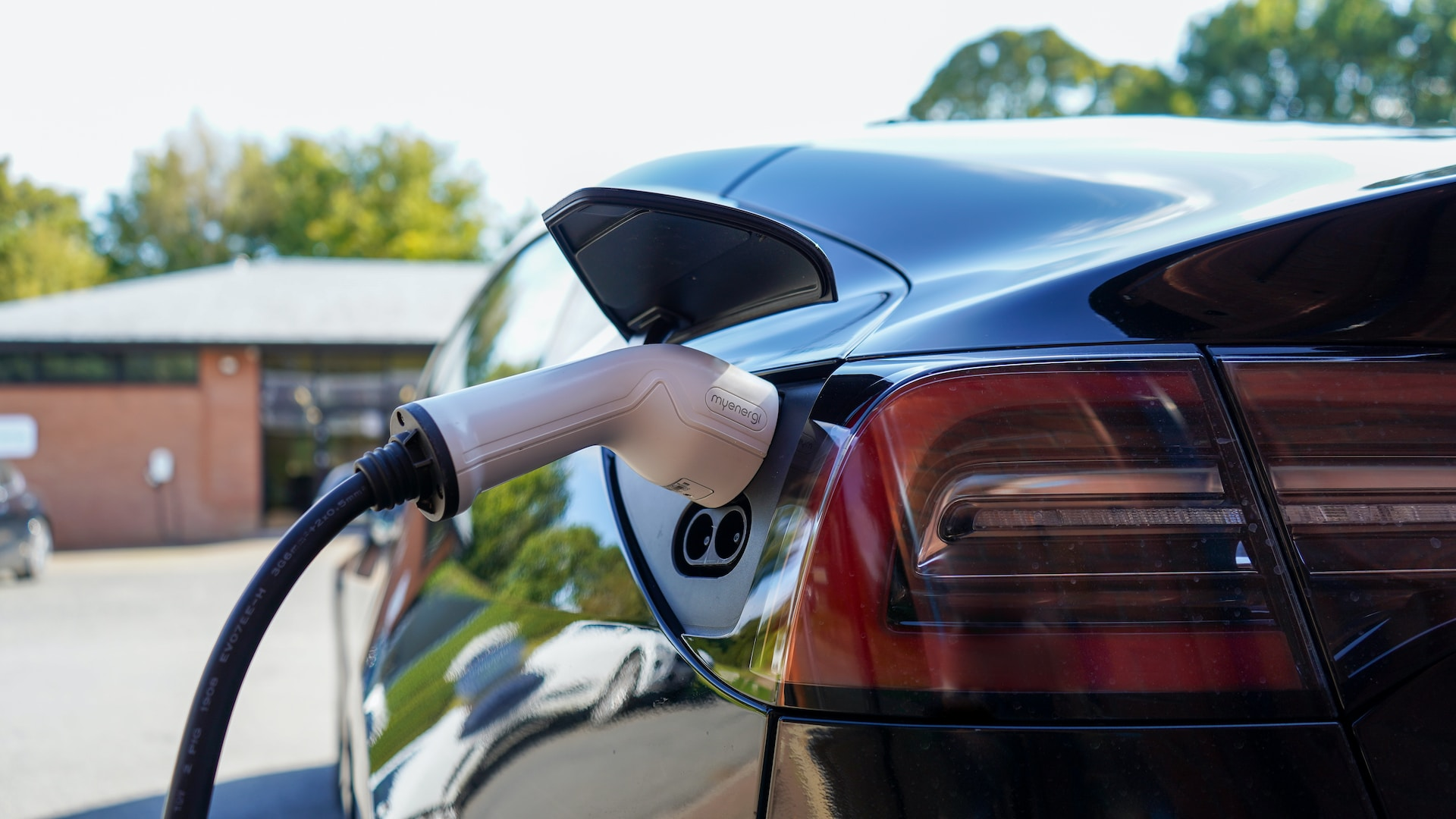

Choosing the right home charging solution is essential for maximizing the efficiency and convenience of your EV charging experience. In this section, we’ll help you evaluate your charging needs and choose between Level 1 and Level 2 home charging options based on factors such as daily mileage, available electrical service, and charging time requirements.
Level 1 charging is the most basic and affordable option, and is suitable for those who drive short.
Evaluating Your Needs
When selecting a home charging solution, it’s important to consider various factors, including:
- The range needs of your EV
- The charging rate
- The installation cost
- The security of the charger
Assessing your daily mileage and the distance you need to travel can help you determine whether a Level 1 or Level 2 charger is the most suitable option for your needs.
Additionally, when choosing an EV charger, consider the following factors:
- Charging speed: Look for a charger with a high kilowatt (kW) rating to ensure fast charging for your EV.
- Certification and safety standards: Make sure the charger is certified and meets all necessary safety standards.
- Cost of installation: Factor in the cost of installation when budgeting for your EV charger.
Level 2 Home Charging Incentives
To make Level 2 home charging more affordable, several utility providers and air districts in California offer rebates. Furthermore, a federal tax credit provides individuals with 30% off a ChargePoint Home Flex electric vehicle charging station plus installation costs (up to $1,000).
Additional incentives are available through various utility companies and programs, making Level 2 home charging an attractive option for many EV owners. By taking advantage of these incentives and tax credits, you can significantly reduce the cost of purchasing and installing Level 2 home charging equipment.
This can make upgrading from Level 1 to Level 2 charging a more financially viable option, allowing you to enjoy faster and more convenient charging at home.
Public and Workplace Charging: Accessibility and Costs
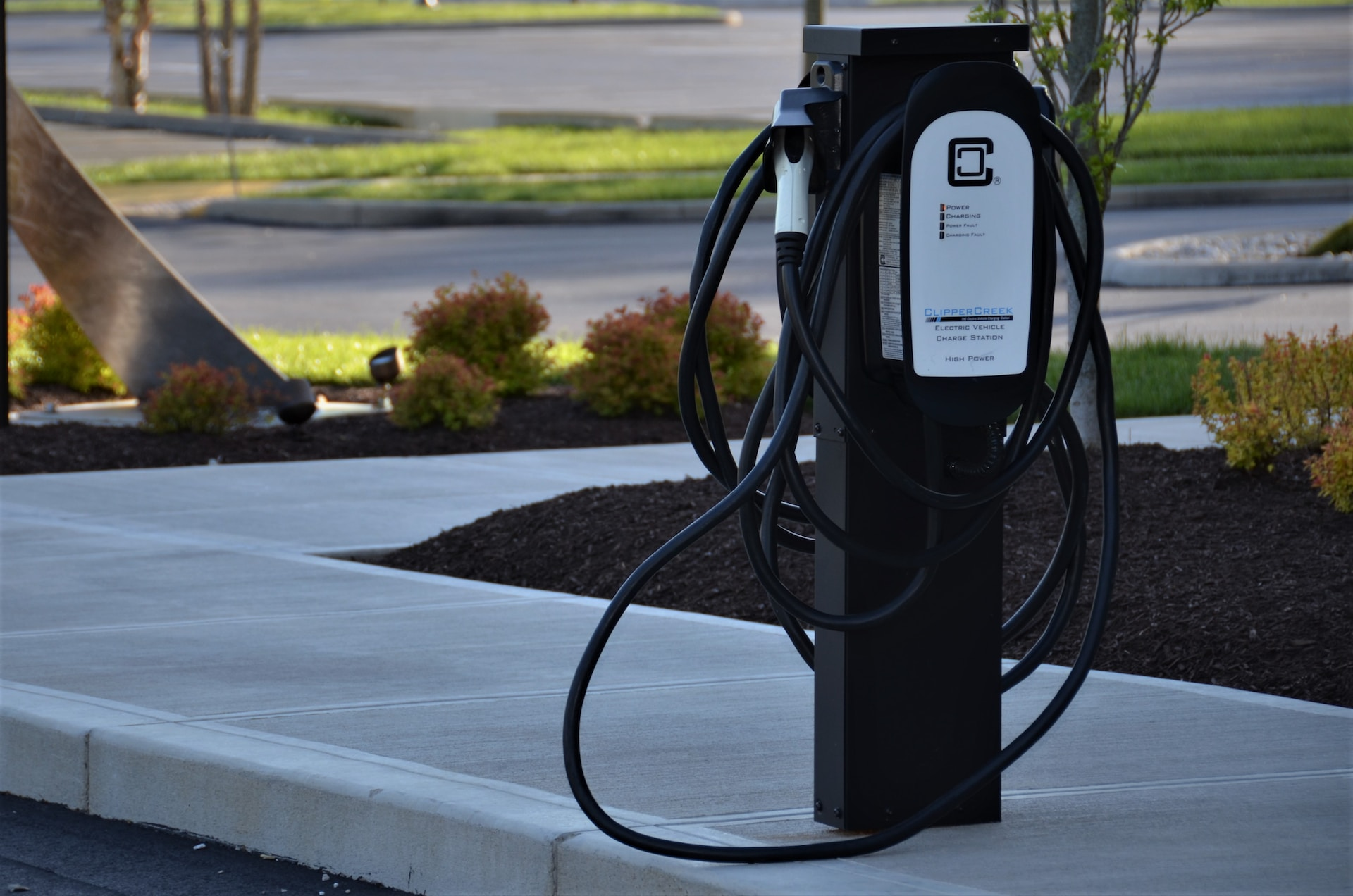

Public and workplace charging options are essential for EV owners, providing additional charging opportunities beyond home charging. In this section, we’ll discuss the accessibility and costs of public and workplace charging.
We’ll also look at how to locate charging stations, ensuring you’re well-equipped to charge your EV in any situation.
Finding Public Charging Stations
With over 130,000 public charging locations in the US, finding a charging station is easier than ever. To locate public charging stations, you can use tools and apps like ChargeHub’s charging stations map, available on iOS, Android, and web browsers.

These apps not only help you find charging stations nearby but also provide real-time status updates and location information. Whether you’re planning a long road trip or simply need a quick charge, these tools ensure you can always find a charging station when you need one.
Understanding Charging Costs
The costs of public and workplace charging can vary depending on the location and provider of the charging station. Some factors to consider include:
- Some employers may offer free charging for a limited time
- Others may charge a fee per hour
- Public charging stations may charge based on the cost of electricity or the amount of time spent charging
- Costs can range between $10 and $30
To help offset these costs, many EV charging networks offer discounted charging when you sign up for a monthly or yearly service plan that involves a fee. By understanding the costs associated with public and workplace charging, you can make informed decisions about which charging options are most suitable for your needs and budget.
Future Developments in EV Charging
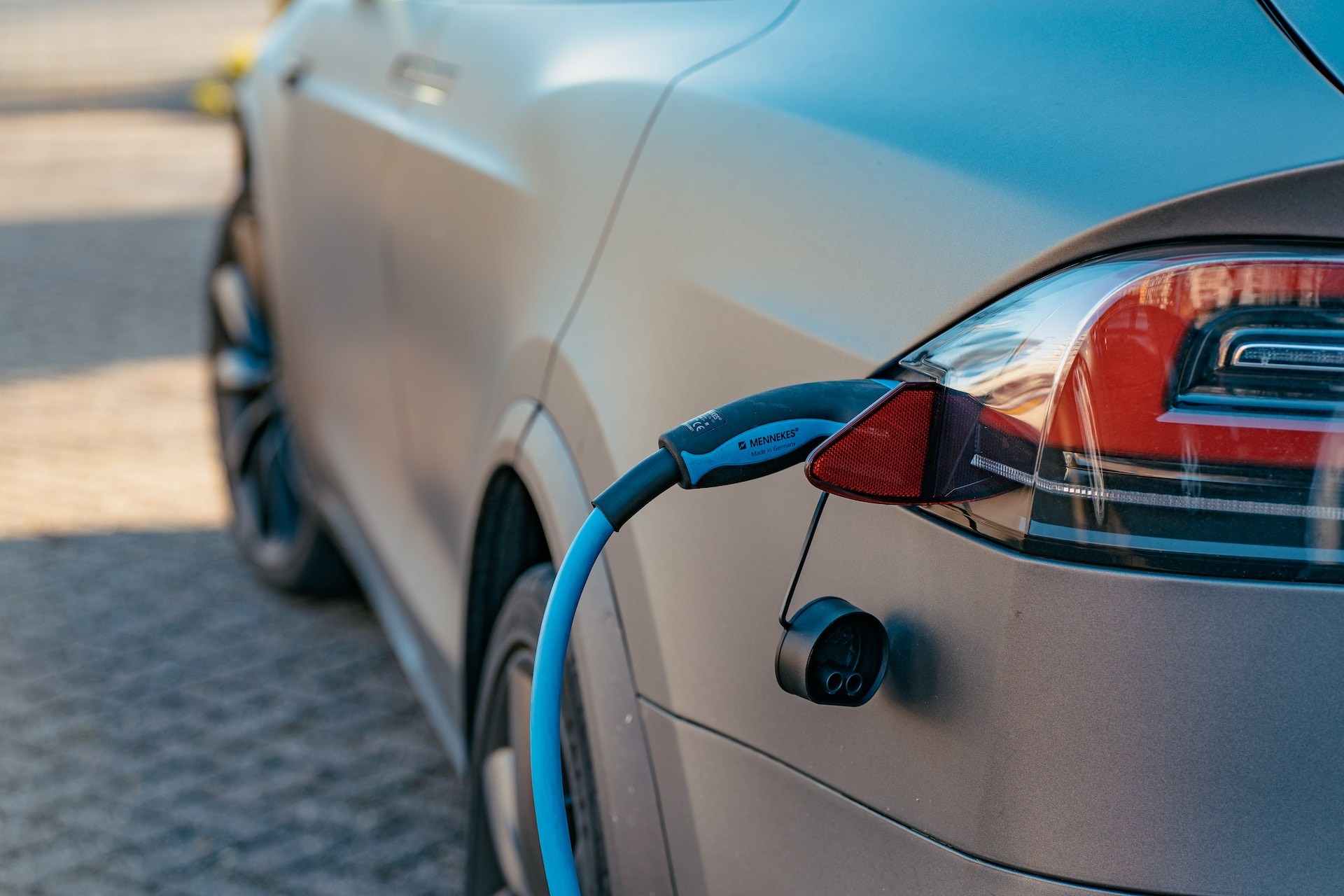

As EV technology continues to advance, new developments in EV charging are emerging, including high-power AC charging, extreme fast charging (XFC), and inductive charging. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize the way we charge our vehicles, making them more convenient and accessible than ever before. With the integration of electric vehicle supply equipment alongside electric vehicle service equipment, the future of EV charging and EV battery technology looks promising.
High-power AC charging allows for faster charging times, while XFC can charge a vehicle.
High-Power AC Charging: SAE J3068 Standard
The SAE J3068 standard outlines the specifications for higher rates of AC charging using three-phase power, including the combined charging system. This standard targets power levels ranging from 6 kW to 130 kW, offering faster charging speeds for compatible EVs. In the US, there are two common three-phase voltage configurations. The first is 208/120 V and the second is 480/277 V.

By implementing the SAE J3068 standard, EV charging infrastructure can be improved to accommodate the growing demand for faster charging solutions. This development has the potential to enhance the charging experience for EV drivers, making charging more convenient and efficient.
Extreme Fast Charging (XFC)
Extreme fast charging (XFC) is a technology capable of providing power outputs of up to 350 kW and above, increasingly being installed in the US for heavy-duty vehicle applications such as electric buses. The Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office is highly engaged in researching technology-related issues which could hinder the implementation of XFC charging networks in the United States. They are looking for solutions to bridge the gaps.
As XFC technology continues to develop, it offers a comprehensive charging solution for heavy-duty vehicles, facilitating in-route charging and reducing downtime. The adoption of XFC chargers in the US has the potential to greatly impact the EV charging landscape, making long-range travel more accessible for EV drivers.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the various EV charging levels, connector types, and future developments in charging technology is essential for making the most of your electric vehicle experience. By staying informed and making the right choices for your charging needs, you can maximize the efficiency and convenience of your EV, both at home and on the road. Embrace the electric revolution and enjoy the benefits of clean, sustainable transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Level 1, 2, and 3 EV charging stations?
Level 1 EV charging stations provide a slow charge for electric vehicles, typically taking up to 10 hours to fully charge a car.
Level 2 chargers are much faster, usually able to completely recharge an electric vehicle in 6-12 hours.
Finally, level 3 chargers are the fastest, able to charge a vehicle up to 80% in under 30 minutes. Therefore, the main difference between Level 1, 2, and 3 EV charging stations is the speed at which they can recharge an electric vehicle.
What is a Level 4 charger?
A Level 4 charger is a type of fast-charging station specifically designed for use with Tesla electric vehicles. It utilizes a direct current (DC) supply, which allows the Tesla to charge at higher voltage and up to 20 times faster than a regular wall socket or level 1 or 2 chargers.
This makes it ideal for people who need to quickly top up their battery while on the go.
What are the three primary EV charging levels?
Electric vehicles have three distinct charging levels: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. These levels provide a range of charging speeds, from slowest with Level 1 to fastest with Level 3.
Understanding each one is key for any EV owner.
What is the universal connector for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America?
In North America, Level 1 and Level 2 charging is supported by the universal J1772 connector.
Are Tesla connectors compatible with non-Tesla EVs?
Unfortunately, Tesla connectors are only designed to be used with Tesla EVs and cannot be used with non-Tesla EVs.








